This blog post is tailored for cybersecurity and executive teams in the Electricity Subsector, particularly the E-ISAC (Electricity Information Sharing and Analysis Center) community. Using recent findings on supply chain vulnerabilities in Chinese-manufactured solar inverters as a case study, it explores how Generative AI (GenAI) can support electric utilities in identifying and mitigating cybersecurity risks and strengthening workforce training.
Through eight real-world use cases, we demonstrate how E-ISAC members can apply GenAI tools to enhance cyber situational awareness and operational readiness. Each use case features screen captures from our customized ChatGPT instance, highlighting source-link verification, multiple LLM cross-checks, and domain-specific prompts to increase confidence in the results.
Highlights:
- Sector Context: Overview of U.S. Electric Power segment, including utility types, generation capacity, and regulatory bodies.
- Tactical Use-cases: Flash reporting, research summarization, threat actor profiling, telemetry analysis, and GridEx planning.
- Strategic use-cases: Supply chain sourcing and workforce upskilling.
- Outlook: Manage supply can risk, Commit to cybersecurity fundamentals, invest in workforce GenAI training
Sector Overview
The Electric Power sector comprises over 3,000 organizations under NAICS code 2211, of which 80% is privately owned.
The U.S. electric utility sector includes three main ownership types:
- Investor-Owned Utilities (IOUs): Approximately 187 IOUs serve about 68% of electricity customers.
- Public Power Utilities: Over 2,000 systems operate across 49 states and Puerto Rico, serving around 15% of customers.
- Rural Electric Cooperatives: Roughly 876 cooperatives provide service to approximately 13% of customers.
As of 2024, solar power accounted for approximately 7% of total U.S. electricity generation, with about 72% from utility-scale sources and 28% from small-scale residential and commercial systems [8–15].
NERC (North American Electric Reliability Corporation) develops and enforces security standards to ensure the reliability of the bulk power system. E-ISAC (Electricity Information Sharing and Analysis Center) operated by NERC, serves as the sector’s primary hub for security communication. It supports a secure member portal and a 24×7 Watch Center, which in 2023:
- Supported more than 7,100 users from over 1,400 member organizations.
- Shared intelligence on 968 items, including 240 vulnerabilities, 254 phishing attacks, 123 ransomware incidents, and 37 China-related cyber events. [17]
E-ISAC works closely with cross-sector ISACs including – the WaterISAC, MS-ISAC (Multi-State ISAC), and Communications ISAC – as well as with industry and international partners, key federal agencies such as the DOE, FBI, CISA, DoD, and members of the Intelligence Community.
Use-cases: Tactical
This section describes five use-cases. For each use-case, we show partial screen-captures of ‘AI assistants’ for cybersecurity. The screenshots were generated by iterative prompt dialogs using our ‘ThreatShare.ai Cyber Researcher’ implementation of OpenAI’s ChatGPT 4o, customized for the cybersecurity domain. Our custom implementation is designed to manage GenAI hallucinations using source-link verification to citations mechanisms.
Flash Report
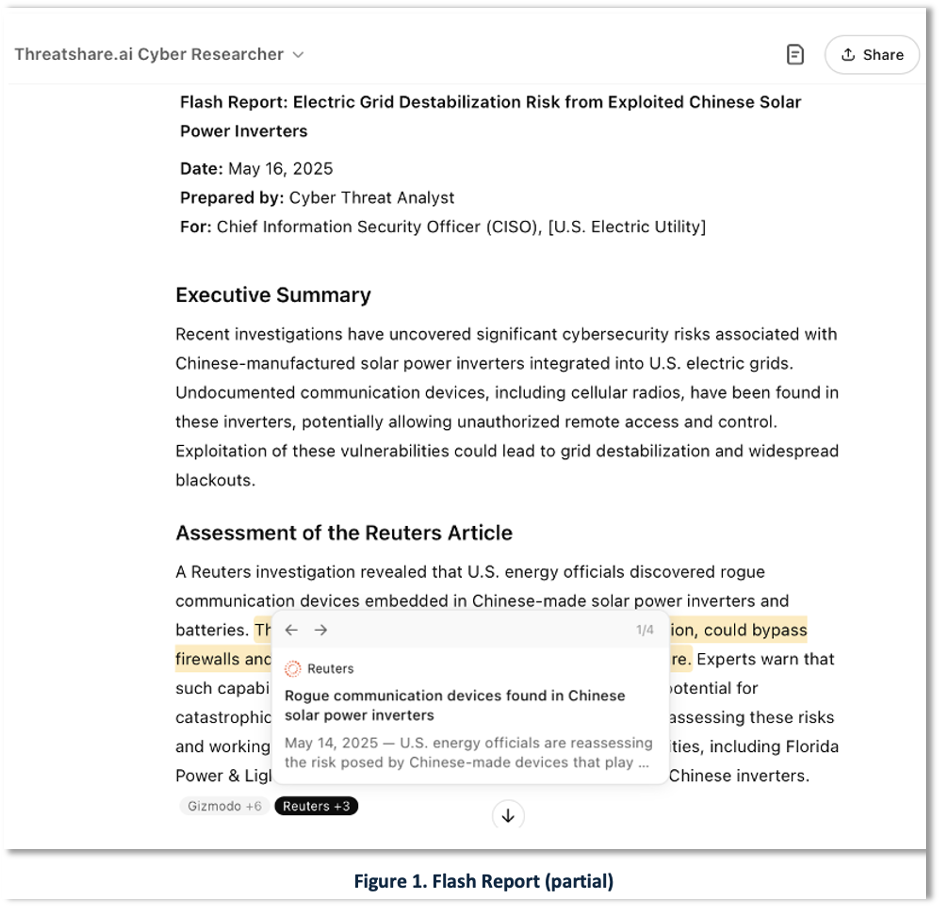
Flash Reports are quick-response, intelligence products that summarize urgent threats. Based on prior experience as E-ISAC contractors, we present a real-world use case inspired by a recent Reuters report on rogue communication devices in Chinese solar inverters and undocumented cellular radios in Chinese batteries. In our scenario, this news could prompt a CISO to issue an RFI and initiate a series of follow-up requests to their cybersecurity team [1].
Acting on the RFI, an analyst uses our GenAI tool to generate a 1-page Flash Report, as shown in Figure 1. The ‘source-link verification’ pop-up allows analysts and readers to quickly assess the link’s relevance and authority.
Summarization
Our second use case demonstrates another practical application of GenAI: summarizing technical reports. Analysts operate under tight deadlines, often reviewing multiple lengthy and complex documents to extract key findings and synthesize insights.
Continuing the scenario, the CISO issues a follow-up RFI requesting additional detail. Using our custom GPT instance to research further sources, the analyst collects over 60 pages of recent technical content from Forescout Research [2], Cyble) [3], and a 2024 FBI Joint Cyber Advisory [4] reports. Forescout reported 45 vulnerabilities across two Chinese inverter brands and discussed prior research on the Chinese threat actor Flax Typhoon. Cyble linked the Russian group “Just Evil” to attacks on Lithuanian energy targets, while the FBI detailed indicators associated with a botnet operated by the Chinese state-sponsored actor Salt Typhoon.
Figure 2 shows a partial view of the resulting two-page summary report. The summary includes a highlighted reference to the Cyble report.
Adversary Landscape
Defending networks requires understanding threat actor motivations, methods, tools, and infrastructure— as well as insights into the target’s attack surface, assets, and vulnerabilities. Cybersecurity teams rely on Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) as a foundational knowledge source. With so many CTI formats and providers, staying current can be overwhelming and costly.
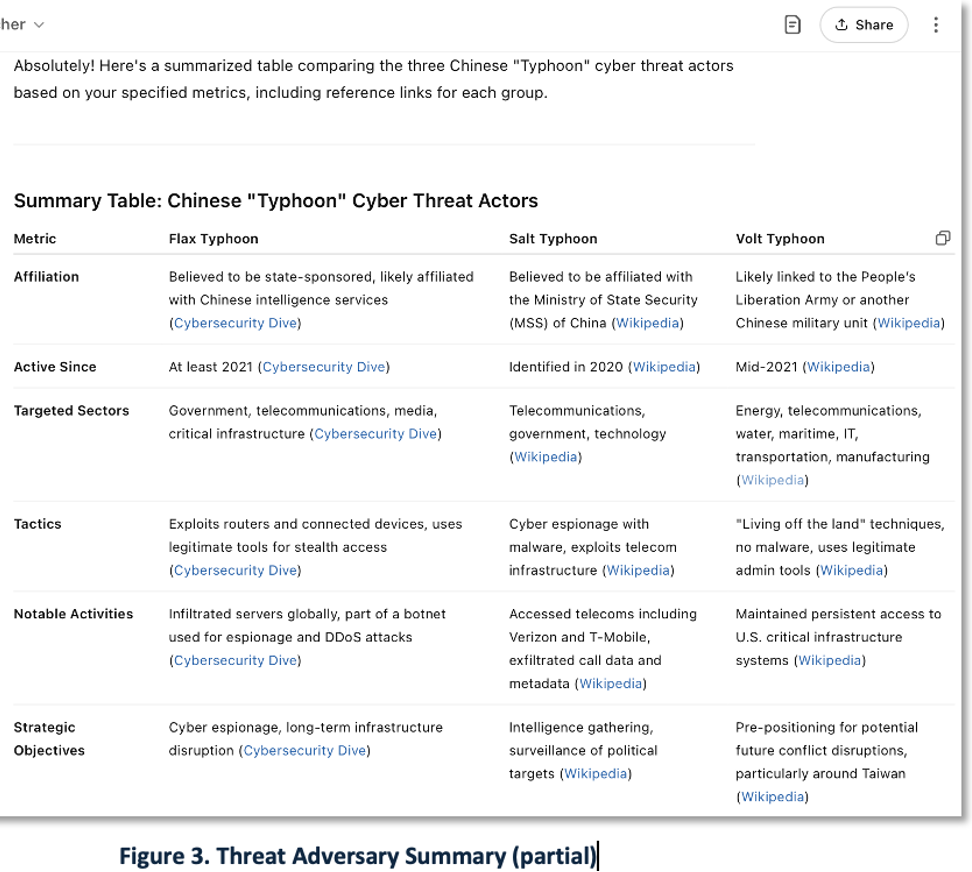
Continuing with our scenario, the CISO issues another RFI requesting a summary of the Chinese “Typhoon” threat actor family, including Flax Typhoon, Volt Typhoon, and Salt Typhoon.
In response, the analyst uses a GenAI tool to generate a structured summary from unstructured sources such as PDFs and HTML pages, as shown in Figure 3.
Network Telemetry
Continuing the scenario, the CISO issues another RFI to the Security Operations Center (SOC) team, requesting an assessment using their CRISP system in response to the latest threat intelligence.
Network telemetry is a vital source of data for cybersecurity teams. E-ISAC and its members rely on the Department of Energy’s CRISP (Cybersecurity Risk Information Sharing Program ) system to collect, analyze, and share data and indicators of compromise (IOCs) derived from network traffic.
CTI that includes network indicators can be integrated into CRISP workflows. For instance, Forescout Research highlighted threats to operational technology (OT) devices, while the FBI Joint Cyber Advisory listed nearly 200 IP addresses and subdomain names linked to Flax Typhoon.
Figure 4 shows a report generated by our GenAI tool. While Forescout did not provide specific network indicators usable by CRISP, the system could still be leveraged to monitor traffic on ports associated with the Modbus and DNP3 protocols — commonly used by OT and IoT devices, including solar power inverters.
GridEx VIII Planning
GridEx is a biennial grid security exercise hosted by E-ISAC, designed to help E-ISAC member and partner organizations practice coordinated response and recovery efforts in the face of cyber and physical security threats. GridEx VIII is scheduled for Nov. 18-19, 2025.
Exercise planning represents another valuable use case for GenAI. Figure 5 shows a partial example of exercise scenarios drawn from a three-page planner generated using our GenAI tool. The full planning document included five scenario themes, listed below. The first scenario draws from Reuters’ – Ghost Machine reporting. Here are the five recommended scenarios:
- Exploited Renewable Energy Devices in Distributed Energy Resources (DERs).
- Grid Telemetry Disruption via Compromised ICCP Systems (Inter-Control Center Communications protocol (ICCP or IEC 60870/TASE.2).
- Coordinated Cyber-Physical Attacks on Interdependent Infrastructure.
- Communications Breakdown in a Hybrid Work Environment.
- Market Disruption and Emergency Dispatch Frameworks
Use-cases: Strategic
Supply Chain Sourcing
China dominates global solar inverter production, with an estimated 80% share of global solar panel production [2, 5, 22]. The European Solar Manufacturing Council (ESMC) has recommended banning Chinese inverters across all EU Member States, following Lithuania’s proactive legislation [5].
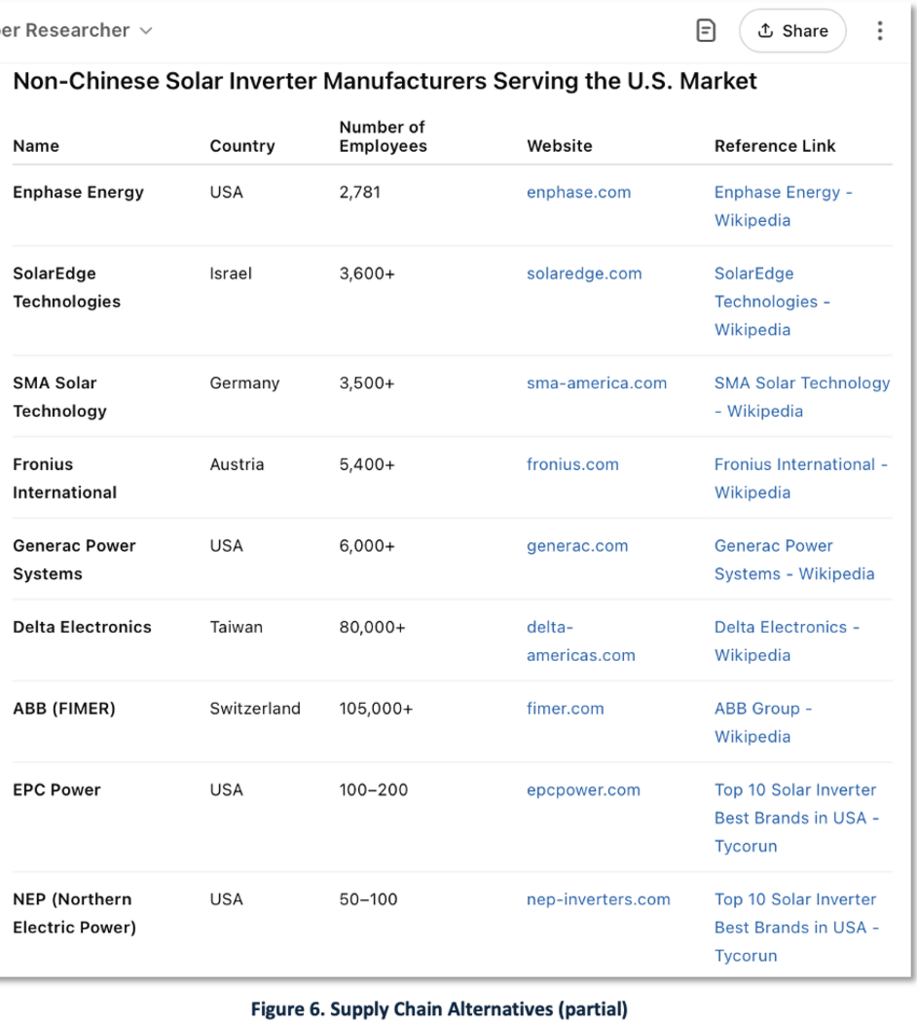
Given this market dominance, combined with China’s status as a major geopolitical rival and its well-documented history of cyberattacks and industrial espionage, one strategic response would be to build alternative supply chains. GenAI can assist planners in exploring and developing alternative sourcing strategies, as demonstrated in the summary report shown in Figure 6.
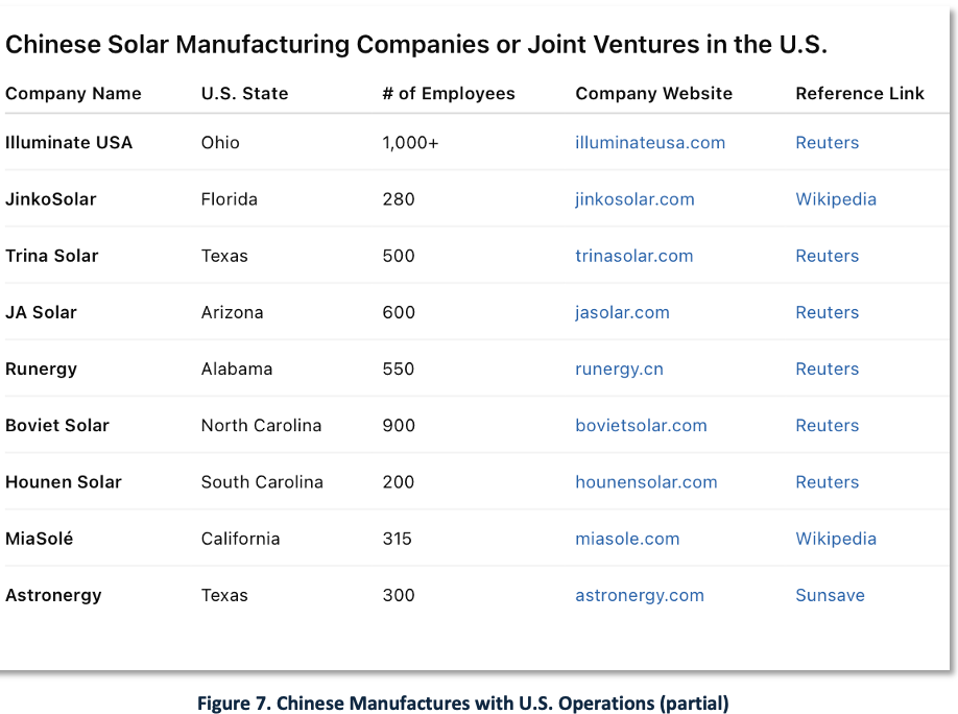
Sourcing decisions are inherently complex and strategic. Many Chinese manufacturers operate in the U.S. through subsidiaries or joint ventures. To help address this issue, we also asked our GenAI tool to generate a list of Chinese operations based in the U.S., as shown in Figure 7. (Note: These references are illustrative and should be independently verified.)
Workforce Training and Upskilling
The power sector faces a retirement cliff, with nearly half the workforce expected to exit within a decade [24]. Organizations are under increasing pressure to invest in training programs in areas such as digital literacy, cybersecurity, and AI applications — including scenario-based exercises.
The need for AI training and its applications in cybersecurity is recognized by NERC [18], which states:
“this white paper asserts that AI/ML systems – if properly scoped, developed, implemented, and monitored and enacted with proper training and continuous improvement – can augment the efforts of dedicated, engaged, and talented real-time system operators to increase the reliability, robustness, and resilience of the BPS <Bulk Power System> … Applications for the use of AI in cybersecurity include access log analysis, phishing prevention, malspam email, detection, and the automation of malware analysis.”
Figure 8 shows a partial screen capture illustrating how companies can use GenAI to explore strategic issues, initiatives, trends, and programs relevant to workforce development and training in the industry.
Outlook
Manage Supply Chain Risk
Supply chain diversification is difficult and slow. As data center demand grows, dependencies on Chinese components persist. Cybersecurity improvements must be applied across existing hardware.
Commit to Cybersecurity Fundamentals
Forescout, Cyble, and FBI advisories consistently recommend network segmentation, patching, monitoring, and authentication as core practices.
Invest in Workforce and AI Training
GenAI can be a game-changer for workforce augmentation, but only when paired with critical thinking, prompt engineering skills, and domain knowledge. AI outputs require verification and structured oversight.
Editor’s Notes:
- Thanks to our GenAI assistants: ChatGPT-4o, ThreatShare.ai Cyber Researcher, Google Gemini AI, and Perplexity.
- Thanks for the featured image to ESMC (European Solar Manufacturing Council)
References
- Reuters – Rogue communication devices found in Chinese solar power inverters, 14-May-2025
- Forescout Research | Vedere Labs: Sun:Down – Destabilizing the Grid via Exploitation of Solar Power Systems, 27-March-2025
- Cyble – Solar Monitoring Solutions in Hacktivists’ Crosshairs, 20-Sept-2024
- FBI Joint Cybersecurity Advisory, Product ID: JCSA-20240918-001 – People’s Republic of China-Linked Actors Compromise Routers and IoT Devices for Botnet Operations, 18-Sept-2024
- ESMC Solar (European Solar Manufacturing Council), Restrict Remote Access of PV Inverters from High-Risk Vendors , 30-April-2025
- Industrial Cyber – Forescout SUN:DOWN research uncovers critical vulnerabilities in solar inverters that threaten power grid stability, 27-March-2025
- Industrial Cyber – FBI warns of increased cyber threats to expanding US renewable energy sector , 2-July-2024
- CISA Energy Sector – https://www.cisa.gov/topics/critical-infrastructure-security-and-resilience/critical-infrastructure-sectors/energy-sector
- LPPC (Large Public Power Council) – Members
- Edison Electric Institute – Industry Data
- American Public Power Association – Stats and Facts
- 2023 E-ISAC End-of-Year Report
- North American Electric Reliability Corporation (NERC) – About NERC
- Electricity Information Sharing and Analysis Center (E-ISAC) – About the E-ISAC
- SEIA (Solar Energy Industries Association) – Solar Market Insight Report 2024 Year in Review
- Afore – Top 20 Solar Inverter Manufacturers: A Global Overview of the Leading Solar Inverter Manufacturers, 26-Nov-2024
- E-ISAC – 2023 E-ISAC End-of-Year Report, 15-Feb-2024
- NERC – Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning in Real-Time System Operations, White Paper Revision 1, November 2024
- CERTRACE – A Primer on NERC’s Reliability Standards., 20-Dec-2022
- ESCC (Electricity Subsector Coordinating Council): https://www.electricitysubsector.org/
- TechCrunch – Google inks another massive solar power deal to electrify its data centers, 19-May-2025
- Supply Chain Digital – How is China Reshaping the Energy Supply Chain?, 27-Nov-2024
- CarbonBrief – Analysis: Clean energy just put China’s CO2 emissions into reverse for first time, 15-May-2025
- TechTarget | Industry Dive – Navigating 4 key trends and challenges shaping the power industry., 7-May-2025
- MIT Technology Review – How AI is introducing errors into courtrooms, 20-May-2025